Data Types
Dr. Mine Dogucu
Variables
Variables
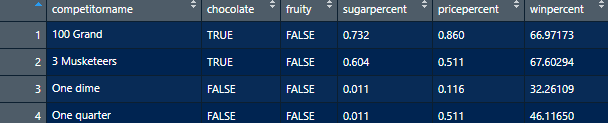
Variables n_kids (number of kids), height, and winpercent are numerical variables.
Variables
Variables n_kids (number of kids), height, and winpercent are numerical variables.
We can do certain analyses using these variables such as finding an average winpercent or the maximum or minimum winpercent.
Variables
Variables n_kids (number of kids), height, and winpercent are numerical variables.
We can do certain analyses using these variables such as finding an average winpercent or the maximum or minimum winpercent.
Not everything represented by numbers represents a numeric quantity. e.g. Student ID, cell phone number.
Variables
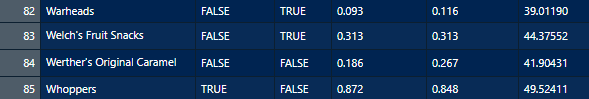
Variables such as chocolate, fruity, and class_year (first-year, sophomore, junior, senior) are categorical variables.
Variables
Variables such as chocolate, fruity, and class_year (first-year, sophomore, junior, senior) are categorical variables.
Categorical variables have levels. For instance chocolate and fruity both have two levels as TRUE and FALSE and class_year have four levels.
glimpse(candy_rankings)## Rows: 85## Columns: 13## $ competitorname <chr> "100 Grand", "3 Musketeers", "One dime", "One quarter…## $ chocolate <lgl> TRUE, TRUE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, TRUE, FALSE, F…## $ fruity <lgl> FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE…## $ caramel <lgl> TRUE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, FALSE,…## $ peanutyalmondy <lgl> FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, TRUE, TRUE, …## $ nougat <lgl> FALSE, TRUE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, FALSE,…## $ crispedricewafer <lgl> TRUE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE…## $ hard <lgl> FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALS…## $ bar <lgl> TRUE, TRUE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, TRUE, FALSE, F…## $ pluribus <lgl> FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE…## $ sugarpercent <dbl> 0.732, 0.604, 0.011, 0.011, 0.906, 0.465, 0.604, 0.31…## $ pricepercent <dbl> 0.860, 0.511, 0.116, 0.511, 0.511, 0.767, 0.767, 0.51…## $ winpercent <dbl> 66.97173, 67.60294, 32.26109, 46.11650, 52.34146, 50.…glimpse(mariokart)## Rows: 143## Columns: 12## $ id <dbl> 150377422259, 260483376854, 320432342985, 280405224677, 17…## $ duration <int> 3, 7, 3, 3, 1, 3, 1, 1, 3, 7, 1, 1, 1, 1, 7, 7, 3, 3, 1, 7…## $ n_bids <int> 20, 13, 16, 18, 20, 19, 13, 15, 29, 8, 15, 15, 13, 16, 6, …## $ cond <fct> new, used, new, new, new, new, used, new, used, used, new,…## $ start_pr <dbl> 0.99, 0.99, 0.99, 0.99, 0.01, 0.99, 0.01, 1.00, 0.99, 19.9…## $ ship_pr <dbl> 4.00, 3.99, 3.50, 0.00, 0.00, 4.00, 0.00, 2.99, 4.00, 4.00…## $ total_pr <dbl> 51.55, 37.04, 45.50, 44.00, 71.00, 45.00, 37.02, 53.99, 47…## $ ship_sp <fct> standard, firstClass, firstClass, standard, media, standar…## $ seller_rate <int> 1580, 365, 998, 7, 820, 270144, 7284, 4858, 27, 201, 4858,…## $ stock_photo <fct> yes, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, yes, yes, …## $ wheels <int> 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2…## $ title <fct> "~~ Wii MARIO KART & WHEEL ~ NINTENDO Wii ~ BRAND NEW …character: takes string values (e.g. a person's name, address)
character: takes string values (e.g. a person's name, address)integer: integer (single precision)
character: takes string values (e.g. a person's name, address)integer: integer (single precision)double: floating decimal (double precision)
character: takes string values (e.g. a person's name, address)integer: integer (single precision)double: floating decimal (double precision)numeric: integer or double
character: takes string values (e.g. a person's name, address)integer: integer (single precision)double: floating decimal (double precision)numeric: integer or doublefactor: categorical variables with different levels
character: takes string values (e.g. a person's name, address)integer: integer (single precision)double: floating decimal (double precision)numeric: integer or doublefactor: categorical variables with different levelslogical: TRUE (1), FALSE (0)
As a data scientist it is your job to check the type(s) of data that you are working with. Do not assume you will work with clean data frames, with clean names, labels, and types.
glimpse(titanic_train)## Rows: 891## Columns: 12## $ PassengerId <int> 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,…## $ Survived <int> 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1…## $ Pclass <int> 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3…## $ Name <chr> "Braund, Mr. Owen Harris", "Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Fl…## $ Sex <chr> "male", "female", "female", "female", "male", "male", "mal…## $ Age <dbl> 22, 38, 26, 35, 35, NA, 54, 2, 27, 14, 4, 58, 20, 39, 14, …## $ SibSp <int> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 4, 0, 1, 0…## $ Parch <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0…## $ Ticket <chr> "A/5 21171", "PC 17599", "STON/O2. 3101282", "113803", "37…## $ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 71.2833, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 51.8625,…## $ Cabin <chr> "", "C85", "", "C123", "", "", "E46", "", "", "", "G6", "C…## $ Embarked <chr> "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S"…